Symptoms Of Bronchospasm
The symptom of bronchospasm is common in childhood and in winter times. Anyway, we have to know that we are facing a sign that reveals the existence of some pulmonary mechanism that must be studied.
Except in children under two years of age, where bronchospasm is a clinical entity in itself due to the small diameter of the bronchi, in older people basic pathologies must be traced. It could be asthma, COPD, or a developing allergy.
Thus, there is a tendency to distinguish between infants and the rest of the population for the study of this symptom. Even up to two years, its repetition gives it a particular diagnostic name, which is recurrent bronchial syndrome or recurrent obliterative bronchitis.
On the other hand, for those over two years of age there are pre-existing triggers or pathologies that explain the symptom of bronchospasm. Here we include asthmatic children, older adults with emphysema or chronic bronchitis, seasonal fall or spring allergies, and environmental pollution.
What is bronchospasm?
Parents often know what a bronchospasm is because it is a classic symptom of pediatric age. They identify the wheezing that appears when breathing and immediately recognize it as such.
What happens to make that characteristic hiss audible is that the bronchus closes too much and makes the air whistle as it passes through it. It is pure physics that causes the noise.
The reasons for the bronchus to close too much are varied. Sometimes it responds to a reaction to the internal content of the duct, and other times it is an order that comes through the nervous system to contract.
An internal content capable of causing bronchospasm is mucus. The child sometimes starts with a cold with a cough; their glands make mucus that is deposited inside the bronchus and, in the effort to expel that substance, it closes too much. Then, the wheezing and shortness of breath occurs.
On the other hand, an external cause is an agent in the environment that is toxic, such as cigarette smoke. It enters through the nose and mouth, irritating everything in its path, and the nervous system sends the lungs the order to close the air passage so that the pollutant does not reach further inside. Then again, we have wheezing and shortness of breath.
A particular case is bronchospasm associated with exercise and sports. This is supposed to address a response from the internal muscle of the bronchi to mobilization. In asthmatic people, the beginning of sports practice can lead to bronchospasm.
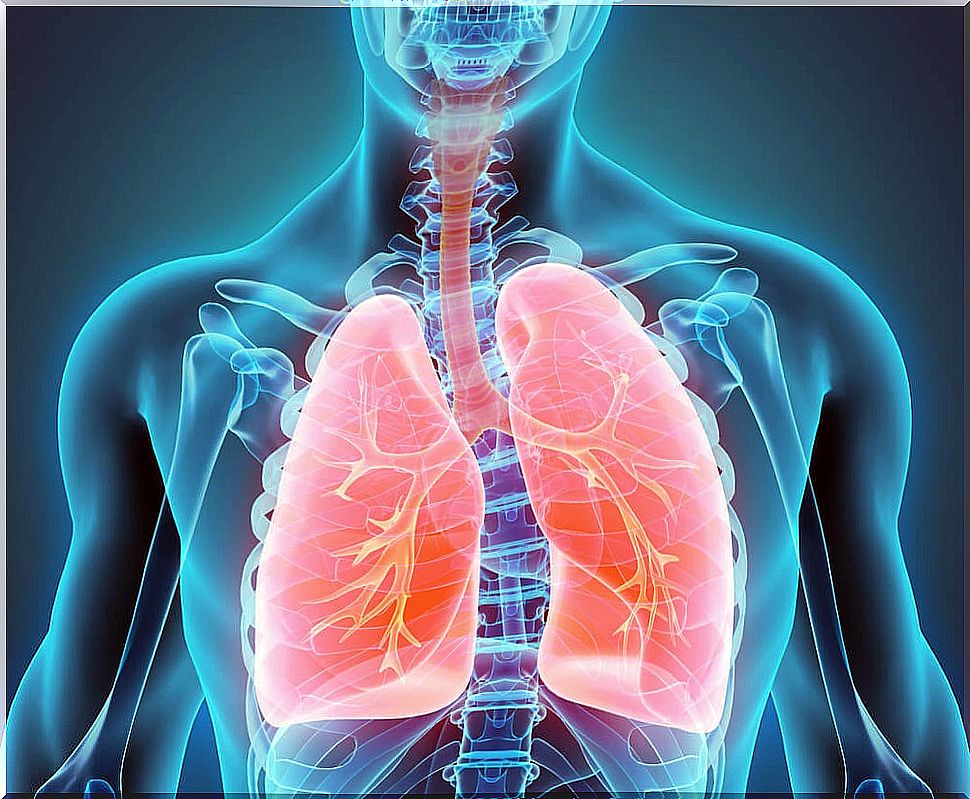
Symptoms of a bronchospasm
The classic symptom of bronchospasm is wheezing. It is a sharp noise that appears, above all, when exhaling, and responds to the passage of air through the narrowing that was formed within the bronchus.
This leads to shortness of breath or dyspnea. The degree of it is variable based on the degree of obstruction, the age of the patient and the underlying diseases that he may have. The shortness of breath of a controlled asthmatic is not the same as that of a one-year-old child.
The cough is characterized by being dry in bronchospasm. Neither can a productive cough be ruled out, as it is impossible to appear, since certain infections occur, at the same time, with excessive wheezing and mucus.
The persistence of the closed bronchus leads to a respiratory effort that is intense. Asthmatic patients understand this well because they suffer from it in crises. Your chest muscles have to work harder than usual to move air into your lungs.
Because of the excessive effort, the pains in the chest ensue. In infants there is an observable sign consisting of the collapse of certain muscles of the chest.

How is it treated and prevented?
Once bronchospasm set in and is ongoing, bronchodilator medication is required. The usual and most effective is the use of inhalers that asthmatics always have on hand. The drug par excellence in this field is salbutamol.
If the symptom does not respond relatively quickly, or signs of severity are added, doctors sometimes prescribe corticosteroids for a short time, to reduce lung inflammation. If there is a concomitant infection, the vast majority are viral.
But it is important to prevent the appearance of bronchospasms. For this, we must eliminate tobacco from homes, feed babies with breastfeeding and ventilate home and office environments.
Attentive in the time of bronchospasm
We must always be attentive to bronchospasm when we have children under 2 years of age or asthmatics. Also older adults who suffer from basic lung diseases. In any case, it is the seasonal changes and winter that have to put us on greater alert.
If we suffer from bronchospasm, we must remain calm and consult with the health professional. In the case of people with asthma, they should have written and memorized the protocol for action with salbutamol in the event of attacks, to apply it if necessary.