Penicillin Allergy
Penicillin is an antibiotic originating from the Penicillium fungus, which belongs to the group of β-lactam antibiotics. There are different types of penicillins but they all have the β-lactam nucleus.
However, each type of penicillin works against bacteria to a different degree. In addition to eliminating bacteria that cause different infections in our body, penicillin serves to prevent infections caused by gram-positive bacteria.
What if you have a penicillin allergy?
Allergy to beta-lactams is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Diagnosis of penicillin allergy is made through medical history and skin tests.
Types of allergic reactions
The classification of allergic reactions to penicillin and, in general, to beta-lactam antibiotics, is based on the time interval between the administration of the drug and the appearance of the reaction.
Immediate allergic reactions
They are those reactions that take place in the first hour after the administration of the drug. They are usually mediated by specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) that very rapidly releases histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
The way it manifests varies from mild reactions, such as hives, angioedema, and wheezing, to severe, such as anaphylactic shock.
Accelerated reactions
These types of reactions appear between two and seventy-two hours after the administration of the antibiotic. Although its mechanism is not well described, there may be reactions such as urticaria, angioedema, laryngeal edema, and wheezing.
Late allergic reactions
They are those that take place from seventy-two hours after the administration of the drug. They are normally mediated by T lymphocytes and manifest in a very diverse way.
Both accelerated and late reactions can be grouped under the term non-immediate reactions. Signs and symptoms of non-immediate reactions include the following:
- Maculopapular or fixed drug eruption.
- Urticaria.
- Erythema multiforme.
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis.
- Exfoliative or contact dermatitis.
- Hypersensitivity syndrome.
- Lichenoid dermatosis.
Fortunately, however, the most common reactions are usually not severe and consist of maculopapular rashes followed by hives.
How is a penicillin allergy diagnosed?
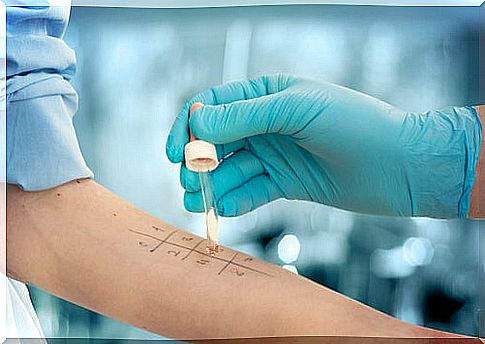
If hypersensitivity is suspected, testing for a penicillin allergy is essential. This is important since adverse reactions are often confused with allergic reactions.
The diagnosis is based on the description of the symptoms and the time elapsed between taking penicillin and the appearance of the reaction, as well as the type of symptoms.
In this way, the type of allergic reaction can be classified as immediate or not immediate. In immediate allergic reactions, it has been found that as the time elapses between the initial reaction and the study, there is less chance of finding a positive skin test.
However, this loss of sensation does not have to be permanent. There is the possibility of resensitization to these antibiotics after doing skin tests or taking the drug again. On the other hand , in non-immediate reactions the phenomenon of loss of sensitivity is not common.
Skin tests to diagnose penicillin allergy
Immediate reactions start with a prick test or allergy skin test on the skin. One or more determinants can be used and, if the answer is negative, the next step is to do an intradermal test.
Both are usually done on the forearm and the reading takes place after 15 to 20 minutes. However, in non-immediate reactions, intradermal tests can be started directly with readings at 20 minutes and at 48 and 72 hours.
While intradermal tests are being done, systemic reactions may appear. This, especially, when many preparations are used at the same time.
Desensitization
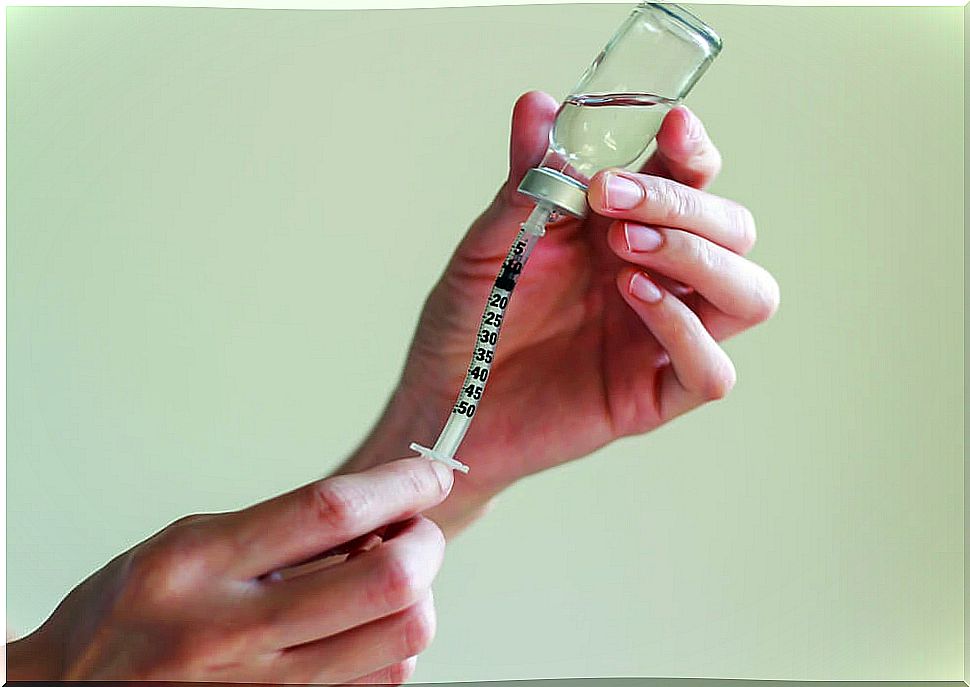
Desensitization consists of the re-administration of the antibiotic that has led to an allergic reaction in progressive doses until the therapeutic dose is reached.
Desensitization is reversible and depends on the continued presence of the antibiotic in the body. It loses its effectiveness when you suspend the administration for a period of more than 48 hours.
Conclution
The antibiotic group of penicillin is prescribed very frequently, and as a result, in sensitized people, allergic reactions occur that can be fatal.
For this reason, it is important to properly and timely diagnose true allergies to antibiotics from pseudo- allergenic reactions.